戴志晖教授课题组在JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN CHEMICAL SOCIETY发表研究论文
Electrochemiluminescence for Electric-Driven Antibacterial Therapeutics
Liu, SS (Liu, Shanshan)[ 1,2 ] ; Yuan, HX (Yuan, Huanxiang)[ 1 ] ; Bai, HT (Bai, Haotian)[ 1 ] ; Zhang, PB (Zhang, Pengbo)[ 1 ] ; Lv, FT (Lv, Fengting)[ 1 ] ; Liu, LB (Liu, Libing)[ 1 ] ; Dai, ZH (Dai, Zhihui)[ 2 ]*(戴志晖); Bao, JC (Bao, Jianchun)[ 2 ] ; Wang, S (Wang, Shu)[ 1 ]*
[ 1 ] Chinese Acad Sci, Beijing Natl Lab Mol Sci, Inst Chem, Key Lab Organ Solids, Beijing 100910, Peoples R China
[ 2 ] Nanjing Normal Univ, Sch Chem & Mat Sci, Nanjing 210023, Jiangsu, Peoples R China
JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN CHEMICAL SOCIETY,201802,140(6),2284-2291
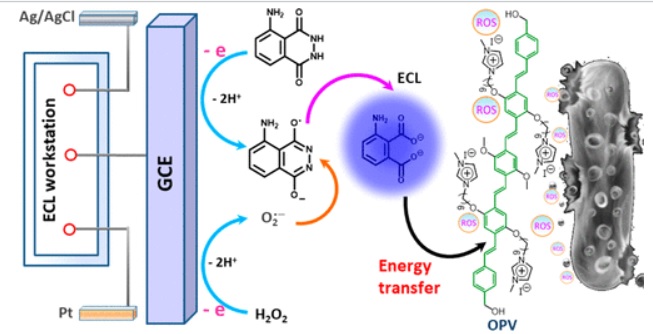
The employment of physical light sources in clinical photodynamic therapy (PDT) system endows it with a crucial defect in the treatment of deeper tissue lesions due to the limited penetration depth of light in biological tissues. In this work, we constructed for the first time an electric driven luminous system based on electrochemiluminescence (ECL) for killing pathogenic bacteria, where ECL is used for the excitation of photosensitizer instead of a physical light source to produce reactive oxygen species (ROS). We named this new strategy as ECL-therapeutics. The mechanism for the ECL-therapeutics is dependent on the perfect spectral overlap and energy transfer from the ECL generated by luminol to photosensitizer, cationic oligo(p-phenylenevinylene) (OPV), to sensitize the surrounding oxygen molecule into ROS. Furthermore, taking into account the practical application of our ECL-therapeutics, we used flexible hydrogel to replace the liquid system to develop hydrogel antibacterial device. Because the chemical reaction is a slow process in the hydrogel, the luminescence could last for more than 10 min after only electrifying for five seconds. This unique persistent luminescence characteristic with long afterglow life makes them suitable for persistent antibacterial applications. Thus, stretchable and persistent hydrogel devices are designed by integrating stretchable hydrogel, persistent ECL and antibacterial function into hydrogel matrices. This novel strategy avoids the employment of external light source, making it simple, convenient and controllable, which exploits a new field for ECL beyond sensors and also opens up a new model for PDT.
文章链接:
https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/jacs.7b12140
版权与免责声明:本网页的内容由收集互联网上公开发布的信息整理获得。目的在于传递信息及分享,并不意味着赞同其观点或证实其真实性,也不构成其他建议。仅提供交流平台,不为其版权负责。如涉及侵权,请联系我们及时修改或删除。邮箱:sales@allpeptide.com