李亚飞教授课题组在ACS ENERGY LETTERS发表研究论文
Insights into Hydrotropic Solubilization for Hybrid Ion Redox Flow Batteries
Ding, Y (Ding, Yu)[ 1,2 ] ; Zhang, CK (Zhang, Changkun)[ 1,2 ] ; Zhang, LY (Zhang, Leyuan)[ 1,2 ] ; Wei, HY (Wei, Haiyan)[ 3 ] ; Li, YF (Li, Yafei)[ 3 ]*(李亚飞); Yu, GH (Yu, Guihua)[ 1,2 ]*
[ 1 ] Univ Texas Austin, Mat Sci & Engn Program, Austin, TX 78712 USA
[ 2 ] Univ Texas Austin, Dept Mech Engn, Austin, TX 78712 USA
[ 3 ] Nanjing Normal Univ, Sch Chem & Mat Sci, Jiangsu Key Lab New Power Batteries, Nanjing 210023, Jiangsu, Peoples R China
ACS ENERGY LETTERS,201811,3(11),2641-2648
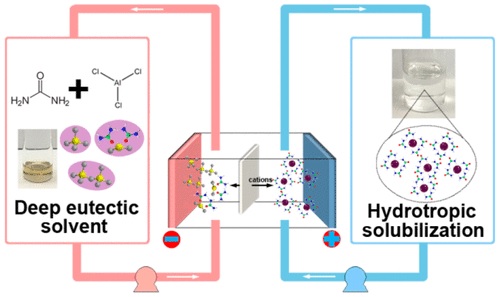
Inspired by the solubility enhancement in pharmaceutical research, we report a redox flow battery enabled by hydrotropic solubilization. An almost 3-fold increase in the solubility of hydroquinone (H(2)BQ)-based catholyte can be achieved by employing urea as a hydrotropic agent, and the universal effect of urea on a variety of organic redox species has been demonstrated as well. By combining chemical characterization and computational modeling, the molecular interactions between solute, solvent, and hydro tropic agent are elucidated to shed light on the hydrotropic mechanism. Moreover, the working potential of the flow battery can be improved by adopting deep eutectic solvents (DESs) as anolytes. The hydrotropic solubilization leads to an energy density of 114 Wh L-1 when pairing the catholyte with a Li anode, and the energy density can still reach 25.3 Wh L-1 in the proof-of-concept hybrid ion flow battery.
文章链接:
https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsenergylett.8b01828
版权与免责声明:本网页的内容由收集互联网上公开发布的信息整理获得。目的在于传递信息及分享,并不意味着赞同其观点或证实其真实性,也不构成其他建议。仅提供交流平台,不为其版权负责。如涉及侵权,请联系我们及时修改或删除。邮箱:sales@allpeptide.com