周林副教授和魏少华教授课题组在SMALL发表研究论文
Drug-Controlled Release Based on Complementary Base Pairing Rules for Photodynamic-Photothermal Synergistic Tumor Treatment
Zhan, QC (Zhan, Qichen)[ 1 ] ; Shi, XQ (Shi, Xianqing)[ 1 ] ; Zhou, JH (Zhou, Jiahong)[ 1 ] ; Zhou, L (Zhou, Lin)[ 1 ]*(周林); Wei, SH (Wei, Shaohua)[ 1 ]*(魏少华)
[ 1 ] Nanjing Normal Univ, Jiangsu Collaborat Innovat Ctr Biomed Funct Mat, Key Lab Appl Photochem, Coll Chem & Mat Sci,Jiangsu Key Lab Biofunct Mat, Nanjing 210023, Jiangsu, Peoples R China
SMALL,201901,15(3)
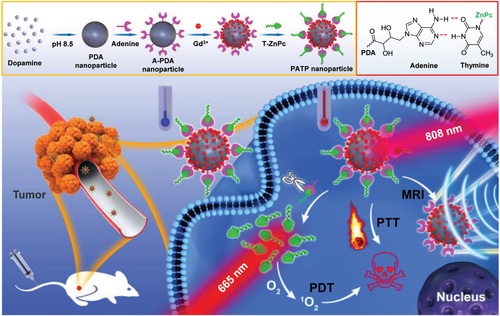
Controlled drug release systems can enhance the safety and availability but avoid the side effect of drugs. Herein, the concept of DNA complementary base pairing rules in biology is used to design and prepare a photothermal-triggered drug release system. Adenine (A) modified polydopamine nanoparticles (A-PDA, photothermal reagent) can effectively bind with thymine (T) modified Zinc phthalocyanine (T-ZnPc, photosensitizer) forming A-PDA = T-ZnPc (PATP) complex based on A = T complementary base pairing rules. Similar to DNA, whose base pairing in double strands will break by heating, T-ZnPc can be effectively released from A-PDA after near infrared irradiation-triggered light-thermal conversion to obtain satisfactory photodynamic-photothermal synergistic tumor treatment. In addition, PDA can carry abundant Gd3+ to provide magnetic resonance imaging guided delivery and theranostic function.
文章链接:
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/smll.201803926
版权与免责声明:本网页的内容由收集互联网上公开发布的信息整理获得。目的在于传递信息及分享,并不意味着赞同其观点或证实其真实性,也不构成其他建议。仅提供交流平台,不为其版权负责。如涉及侵权,请联系我们及时修改或删除。邮箱:sales@allpeptide.com